Winter is in full swing in all parts of the world now. This season can be fun but the cold winds give rise to various winter season health problems.
Here we listed the most common winter health problems along with some tips to prevent them.
List of Winter Season Health Problems
1. Common cold and cough

Most people have cough and cold in spring and winter, although you may get affected by cough and cold during any time of the year. Symptoms of cough and cold appear sudden and manifest as….
- Sore throat
- Stuffy or runny nose
- Congestion
- Coughing (dry)
- Chills
- Fatigue
- Sneezing
- Headaches
- Body aches including muscle aches and joint aches
- Low-grade fever
- Nausea, diarrhea or vomiting common in children than in adults
- People with weak immunity, respiratory conditions pneumonia, bronchitis or asthma may develop.
Treatment
There’s no cure for the common cold. Most cases of the common cold get better without treatment, usually within a week to 10 days. But a cough may linger for a few more days. The best thing you can do is take care of yourself while your body heals. For example, drink plenty of liquids, humidify the air, use saline nasal rinses and get adequate rest.
- Nasal Decongestants: To clear the upper respiratory tract and relieve nasal congestion, hot water vapor and nasal sprays work better. But they should be avoided for children below 6 yrs and old age people.
- Antipyretics (Fever Medication): For treatment of fever consider giving medications such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, others). These are safer alternatives to aspirin.
- Cough syrup: Over-the-counter cough and cold medicines are intended to treat the symptoms of coughs and colds, not the underlying disease.
If you use over-the-counter cough and cold medicines, follow the label directions. Don’t take two medicines with the same ingredient, such as an antihistamine, decongestant or pain reliever. Too much of a single ingredient could lead to an accidental overdose.
4. Antibiotics: Antibiotics are of no use against cold viruses and shouldn’t be used unless there’s a bacterial infection.
5. Analgesics (Pain killers): For a fever, sore throat and headache, adults often turn to OTC acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) or other mild pain relievers such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others).
For children younger than 3 months old, don’t give acetaminophen until your baby has been seen by a doctor. Don’t give ibuprofen to a child younger than 6 months old or to children who are vomiting constantly or are dehydrated.
2. Pneumonia
“Pneumonia is an infection that infects the air sacs in one or both lungs”
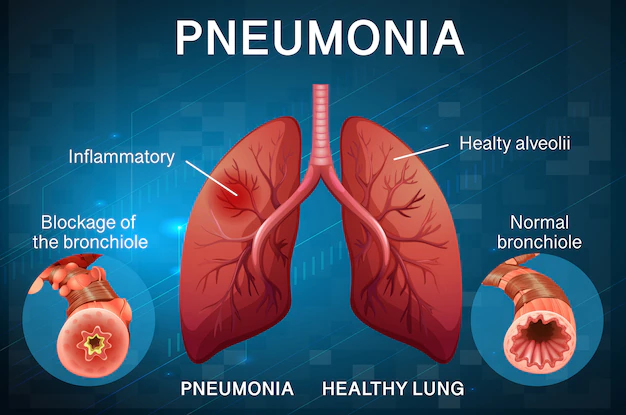
The air sacs may inflame and fill with fluid or pus (purulent material), causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of pneumonia vary from mild to severe, depending on factors such as the type of germ causing the infection, and your age and overall health. Mild signs and symptoms often are similar to those of a cold or flu, but they last longer.
Signs and symptoms of pneumonia may include:
- Chest pain when you breathe or cough
- Confusion or changes in mental awareness (in adults age 65 and older)
- Cough, which may produce phlegm
- Fatigue
- Fever, sweating and shaking chills
- Lower than normal body temperature (in adults older than age 65 and people with weak immune systems)
- Nausea, vomiting or diarrhea
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
Newborns and infants may not show any sign of the infection. Or they may vomit, have a fever and cough, appear restless or tired and without energy, or have difficulty breathing and eating.
Treatment
Treatment for pneumonia involves curing the infection and preventing complications. People who have community-acquired pneumonia usually can be treated at home with medication.
Specific treatments depend on the type and severity of your pneumonia, your age and your overall health. The options include:
- Fever and pain relievers: We can administer some medicines like aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB) and acetaminophen (Paracetamol)
- Cough medicine: Cough suppressors of immense help to loosen and move fluid from the lungs.
- Antibiotics: If you have a bacterial pneumonia, you can try antibiotics as per physician orders.
3. Joint pains
In winters there is a drop in temperature and fall in barometric pressure that affects your joints. These lead to swelling of the cartilage and lining membrane, higher sensitivity of joint pain receptors, tightness of the ligaments and muscles, lack of joint movements due to inactivity and hampered circulation of the nourishing fluid in the joint.
Symptoms of joint pains include…
- swelling
- pain at various areas or spots in the body
- disturbed sleep-waking
- joint stiffness (usually last for 30 mts)
- anxiety
- numbness and tingling of the arms and feet
- headache
- fatigue
Treatment
We can ease joint pains with certain medications like…
- Analgesics (pain killers): parecetamol or non-steroidal anti-inflamatory drugs (diclofenac)
- Muscle relaxants: to reduce joint stiffness they are administered
- Anxiolytics or anti-depressants: if joint pains are of psychological origin, it is better to seek psychiatry specialist advice and administer antidepressants.
Tips to alleviate joint pains
- Keep the ambient temperature warm
- Insulate the limbs with proper clothing or a supporter band
- Wear compression garments or wraps for the joints like the knee
- Regular physical activity even when indoors might help elevate the pain including flexibility and strength training for the muscles
- Proper nutrition is also essential for the joints and muscles with the optimum amount of protein, calcium, and vit C
- Adequate hydration is also essential
- Elevation to the legs helps reduce joint tightness
- Hot compresses or a bath to relax the muscles and warm the limb
- Local application of ointment and massage oils also works wonder
4 Weight gain

Exercising daily may already be a struggle, and adding another obstacle in the form of cold and unruly weather can really extinguish your motivation. The numbers on the scale can tend to creep up during reduced exercise isn’t helped by the rich holiday foods and gatherings that involve large meals.
To best combat weight gain, make a conscious effort to get at least 30 minutes of excercise such as an indoor exercise class to outsmart the elements—at least several times per week.
5. Seasonal depression

The winter blues can have a real effect on people and can cause some seasonal depression. To some extent, these mood changes can be attributed to the decreased sunlight and daylight hours.
To beat the winter blues, make an effort to get natural sunlight during the day and limit your days spent entirely indoors. Also, be sure that you’re getting a proper amount of sleep—about eight hours for most adults.
How to Avoid Winter Season Health Problems?
The winter months can be a little more challenging when it comes to staying healthy. It is important to dress warmly and in layers – as well as stay dry.
Keeping your home free of dust, dirt, pet dander, and other allergens can help reduce asthma symptoms. You should also minimize exposure to cold air by staying indoors when the temperature is extremely low. It’s also important to keep surfaces clean with regular disinfecting to avoid
Here are a few ways you can minimize the risks associated with winter season health problems:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water at regular intervals throughout the day. At least eight 8-ounce glasses per day is typical, but if you’re an active person or live in a cold climate, you may need more.
- Keep your hands clean and avoid touching your eyes, nose or mouth. Wash your hands thoroughly at regular intervals during the day with warm water and soap. If possible, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer to kill germs on those occasions when soap and water aren’t available.
- Avoid close contact with sick people. If someone in your home is ill, keep them away from other family members to minimize the spread of illness. The same goes for friends or co-workers.
- Use hand sanitizer to disinfect frequently touched surfaces at home, work and elsewhere (especially if soap and water aren’t available).
- Get a flu shot each year, if possible. It’s especially important for children and adults over the age of 50.
- Wear thick layers of clothing when outside in colder temperatures to keep out the cold air. You can add or remove these layers as needed based on your activity level to stay comfortable.
- Be active and get adequate nutritious diet and sleep. Avoid stress and anxiety.
Conclusion
Winter can be a difficult time for many people. The ways to stay healthy this season are simple, but it’s important to remember that illness is inevitable.
Disclaimer: The contents of this article are intended to raise awareness about common health issues and should not be viewed as sound medical advice for your specific condition. You should always consult with a licensed medical practitioner prior to following any suggestions outlined in this article or adopting any treatment protocol based on the contents of this article.



