Almost everyone’s had hiccups at one time or another. They usually go away on their own within a few minutes, they can be annoying and interfere with drinking, eating, and talking.
People try endless tricks to get rid of them, from drinking water to eating a spoonful of sugar. But which trick works?
There isn’t much evidence to support the effectiveness of hiccup remedies.
what do mean by the hiccups?
Hiccups are involuntary contractions of the diaphragm muscle, followed by a sudden closure of the vocal cords, resulting in the characteristic “hic” sound.
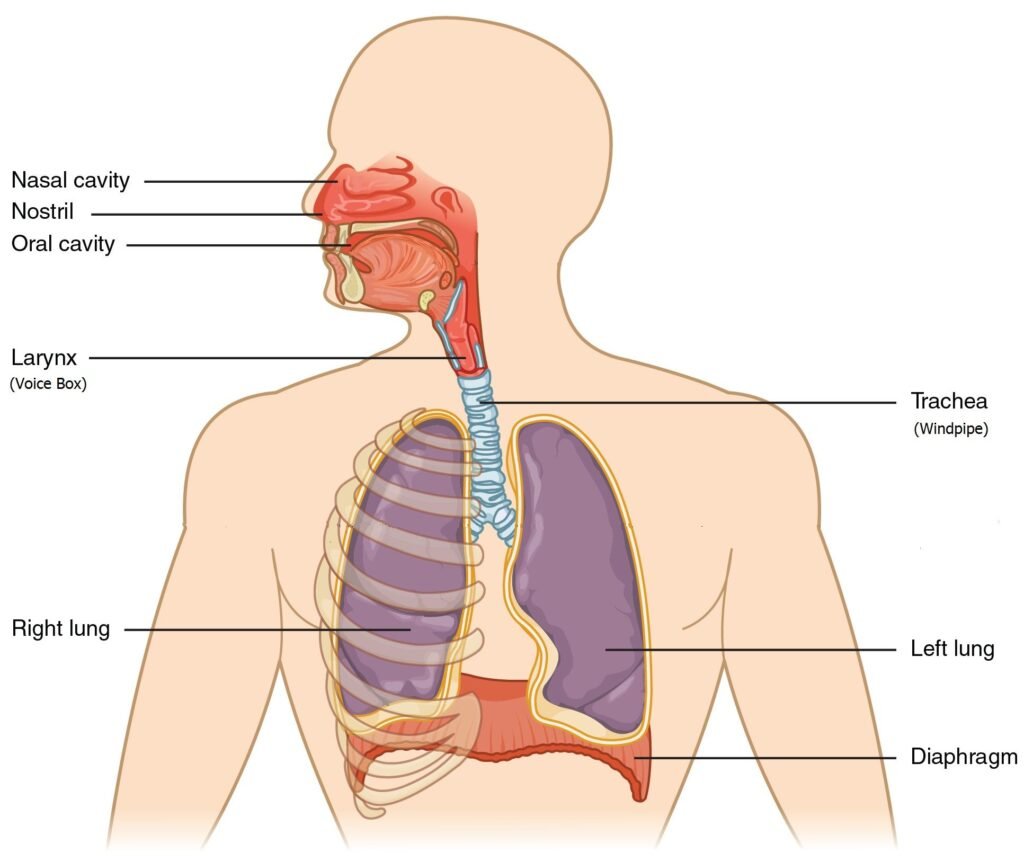
The diaphragm is a large muscle that helps you breathe in and out. When it spasms, you inhale suddenly, and your vocal cords snap shut, which causes a distinctive sound.
Causes:
In most cases, they come and go quickly. Lifestyle factors that may trigger hiccups include:
- Eating too Quickly (May result in swallowed air, leading to hiccups)
- Overeating (Large or spicy meals can irritate the diaphragm, contributing to hiccups)
- Carbonated Beverages (Fizzy drinks can cause the stomach to distend with gas, triggering hiccups)
- Sudden Temperature Changes (Swift transitions from hot to cold or vice versa may stimulate the diaphragm)
- Excitement or Stress (Emotional factors can stimulate the nerves that control the diaphragm)
- Swallowing Air (Activities like chewing gum or smoking can introduce excess air into the digestive system)
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Acid reflux can irritate the diaphragm, leading to hiccups)
- Medical Conditions (Stroke, meningitis, multiple sclerosis, or brain injury).
how to get rid of hiccups?
Read on to learn about the most popular and effective remedies on how to get rid of hiccups.
Drink a Glass of Water:
- Take small sips of cold water.
- Swallow slowly, ensuring that you don’t gulp down the water quickly.
Gargle with Cold Water:
- Gargle with icy water, allowing the cold sensation to stimulate the vagus nerve.
Hold Your Breath:
- Inhale deeply and hold your breath for as long as you can.
- Exhale slowly.
- Repeat this process a few times.
Breathe into a Paper Bag (Cautionary):
- Inhale and exhale into a paper bag, but do this cautiously and briefly.
- This method is not recommended for individuals with certain respiratory conditions.
Swallow a Teaspoon of Sugar:
- Place a teaspoon of sugar on the back of your tongue and let it dissolve.
Hold Your Knees to Your Chest:
- Please sit down and bring your knees to your chest, holding them there for a few moments.
Use an Over-the-Counter Hiccup Remedy:
- Some people find relief from over-the-counter medications designed to alleviate hiccups.
Bend Forward:
- Bend forward at the waist and sip water from the far side of a glass.
Massage the Back of Your Throat:
- Gently rub or massage the back of your throat to stimulate the vagus nerve.
Acupressure:
- Apply gentle pressure to the diaphragm area, located just below the ribcage.
Breathing Exercises:
- Practice slow, deep breaths to relax the diaphragm and control breathing patterns.
Apply Pressure on pressure points:
Applying pressure to these points with your hands may help to relax your diaphragm or stimulate your vagus or phrenic nerves.
- Massage your carotid artery gently. You have a carotid artery on both sides of your neck. It’s what you feel when you check your pulse by touching your neck. Lie down, turn your head to the left, and massage the artery on the right side in a circular motion for 5 to 10 seconds.
- Pull on your tongue. Pulling on your tongue stimulates the nerves and muscles in your throat. Grab the tip of your tongue and gently pull it forward once or twice.
- Squeeze your nose.
Some other remedies to stop hiccups:
Certainly, there are numerous creative and anecdotal remedies that people swear by for stopping hiccups.
Apple Cider Vinegar:
- Consume a teaspoon of apple cider vinegar. Its sour taste may stimulate the vagus nerve, interrupting the hiccup reflex.
Honey:
- Swallow a teaspoon of honey slowly. Its thick consistency might help coat the throat and soothe irritation.
Sucking on a Lemon:
- Suck on a wedge of lemon, biting into it if you can tolerate the sour taste. The strong flavor may help interrupt the hiccup cycle.
Distract Yourself:
- Engage in an activity that requires focus, such as solving a puzzle or counting backward. This distraction may help stop hiccups.
Tickling the Roof of Your Mouth:
- Gently tickle the roof of your mouth with a cotton swab. This may stimulate the vagus nerve and interrupt the hiccup reflex.
Swallowing a Spoonful of Peanut Butter:
- The thick and sticky texture of peanut butter might help reset the diaphragm.
Pulling Your Knees to Your Chest:
- Similar to the method mentioned earlier, sitting down and pulling your knees to your chest can sometimes help stop hiccups.
In addition, some cases of hiccups are more stubborn than others. When this happens, your doctor might prescribe:
- baclofen (Gablofen)
- chlorpromazine (Thorazine)
- metoclopramide

